MAN IN THE MIDDLE ATTACK:
A man in the middle attack (MITM) is a type of cyber attack where an attacker intercepts and alters communication between two users, often to steal sensitive information or eavesdrop on conversation. In computer security, a man in the middle attack is also known as “Hijacking” .
MITM Attack example:
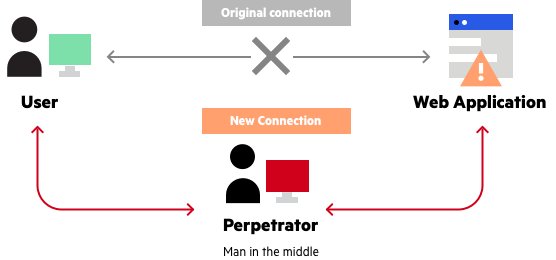
Types of MITM Attack
1.ARP Spoofing
2.DNS Poisoning
3.DHCP Spoofing
4.SSL Stripping
5.Rogue Access Point
6.IP Spoofing
7.Email Hijacking
8.HTTPS Spoofing
- ARP Spoofing: Where an attacker sends fake Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) messages onto a network, associating there own MAC(Media Access Control) Address with the IP Address of a legitimate device, such as router or server in order to intercept, modify or disrupt network traffic.
Example: Suppose we have a network with three devices:
- Victim(192.168.1.100): A laptop connected to the network.
- Gateway(192.168.1.1): The Network router.
- Attacker(193.1681.200): A Malicious device connected to the network.
The attacker want to intercept traffic between the victim and gateway.
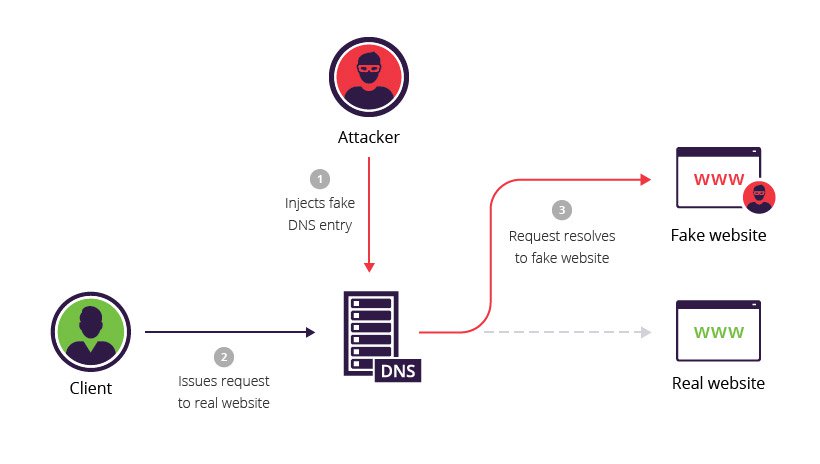
2. DNS Poisoning: When an attacker corrupts the cache of a DNS (Domain Name System) server by replacing the IP Address of a legitimate website or domain with the fake one, and redirecting users to a malicious website.
Example:
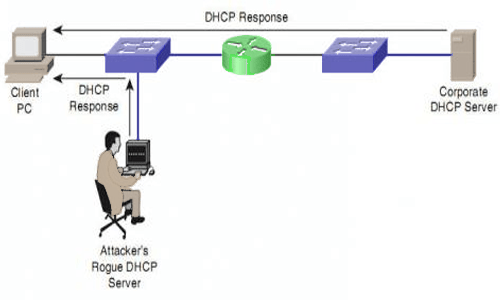
3. DHCP Spoofing: A type of cyber attack where an attacker sends fake DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) messages to a network, pretending to be a legitimate DHCP server, and device accepts the fake DHCP response and configures its IP Addresses and network settings.
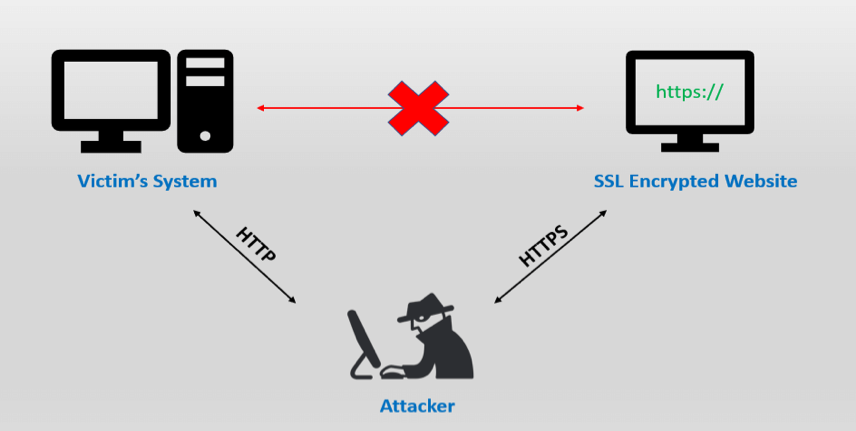
4. SSL Stripping:
SSL stripping is an attack where a malicious actor intercepts an encrypted HTTPS session and downgrades it to an unencrypted HTTP session, allowing the attacker to steal sensitive data. This is done because most websites now use SSL/TLS certificates to encrypt traffic. Without SSL stripping, HTTPS is secure. With SSL stripping, the connection is no longer secure.
5. Rogue Access Point: Rogue access points are a type of malicious wireless device that can be used to intercept and steal sensitive information from devices connected to a wireless network. They can be set up to mimic legitimate access points, allowing attackers to capture and eavesdrop on network traffic.

6.IP Spoofing: IP spoofing is a technique used by attackers to manipulate the source IP address of network packets. It can be used to launch various types of attacks, such as denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, session hijacking, and identity theft.
How IP Spoofing work:
To learn more about Session Hijacking.Click on Read more
7.Email Hijacking: Email hijacking via man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks is a type of phishing attack where an attacker intercepts the communication between an email client and the email server, tricking the client into sending or receiving malicious emails.
How Email Hijacking work:

8. HTTPS Spoofing:HTTPS spoofing is a type of attack where an attacker intercepts and modifies encrypted HTTPS traffic, such as web requests and responses, to trick the user into revealing sensitive information or performing actions on their behalf.
How HTTPS Spoofing works:
How to Prevent MITM Attacks
While MITM attacks are stealthy, there are ways to defend against them:
- Use HTTPS websites – Always check for the padlock icon before entering sensitive data.
- Avoid public Wi-Fi – Or use a trusted VPN when using it.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) – Even if credentials are stolen, 2FA adds an extra layer of security.
- Keep software updated – Patch known vulnerabilities that could be exploited.
- Educate users – Many attacks succeed due to lack of awareness.

0 Comments